PowerPoint
Elements of Accessible PowerPoint Presentations
Themes
Choose themes with good contrast and simple backgrounds. Some of PowerPoint’s built-in themes have low contrast between the text and the background of the slide and others with busy backgrounds, which may make the text difficult to read and navigate.
- To select a theme, go to the Design tab and choose from the many available themes.
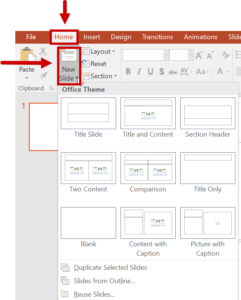
Slide Layouts
When creating new slides in PowerPoint, choose one of the preformatted layouts available. This will ensure that the information presented will have the correct heading structure, list styles, and reading order.
- To create a new slide, select New Slide from the Home tab.
- Select one of the options from the Layout menu.
Alternative Text
- To add alternative text to an image, right-click on the image
and choose Format Picture.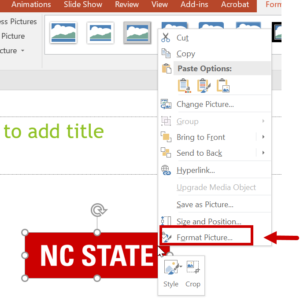
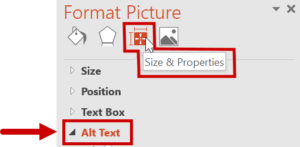
- In the Format Picture sidebar, select the Size & Properties icon.
- Choose Alt Text.
- Enter appropriate alternative text in the Description field.
Tables
- To identify row and column headers in a table, click anywhere in the table.
- The Table Tools options should become visible, and the Design tab should be open.
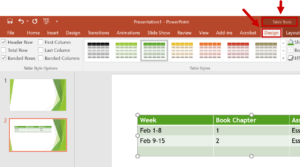
- To make sure the top row of the table will contain column headers (most tables do), mark the Header Row checkbox.
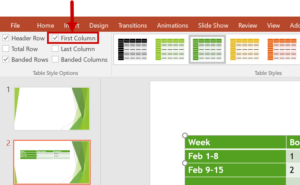
- To make sure the first column of the table will contain row headers, mark the First Column checkbox.
Captions & Translations
- Microsoft Presentation Translator is an add-in that provides real-time subtitles for presentations.
- Subtitles can be shown in the presenter’s language (to support accessibility scenarios) or in any of 60+ supported languages.
- Presentation Translator allows the audience to use their own devices to follow, in their preferred language, what the presenter says.
- Translator requires that the presenter have a microphone.
Installing the Translator
- To install the add-in, visit the Presentation Translator page.
- Select the desired Language.
- Select the Download button and follow the installation instructions.
Using the Translator in a PowerPoint presentation
- Open the desired PowerPoint presentation.
- From the top ribbon, select Slide Show.
Then select Start Subtitles.
NOTE: First-time users will need to Accept the Terms of Use.
- From the dropdown menus, select:
- the language you will be speaking, and
- the language to display in subtitles
- Recommended: To improve the performance of the Translator, mark the checkbox to Customize speech recognition.
- From the Microphone dropdown menu, select your microphone.
- Select Next to continue.
- If you haven’t yet saved your presentation, you will be prompted to do so before you can continue. Click on Save and Start Subtitles.
NOTE: If you are using the Translator for the first time, it may take several minutes for the artificial intelligence to run the setup.
- Before your first slide, a new slide will be inserted. It will display a QR code and instructions in the language you selected.
- As you speak into the microphone, a live transcript of your words will appear on the screen.
PowerPoint Best Practices
- Share accessible PowerPoint presentations in their original PowerPoint file format.
- Use the built-in styles (e.g., Heading Style 1, Heading Style 2) to provide a semantic structure to your document. This will help provide a consistent layout and make the document easier for users of certain assistive technologies to navigate.
- When creating lists, use the built-in bulleted or numbered list feature instead of manually inserting asterisks, numbers, or tabs.
- To add slide numbers, use the Header and Footer dialogue box.
- Use a larger text and minimal word count.
- Use the built-in Accessibility Checker to check for common accessibility issues. Some of the warnings it gives will be subjective, so discernment may be needed.